What is the Difference Between Spam and Phishing?
Spam and phishing have been around since the rise of email as a form of communication. While both are annoying and can clutter your inbox, the two terms are not interchangeable. The big difference between spam and phishing is spam is generally harmless — albeit annoying — while phishing is dangerous and malicious.
What is Spam?
Spam, commonly known as junk mail, is unsolicited or unwanted emails that are usually trying to sell you something. Maybe you attended a trade show and gave your business card to a vendor, who promptly added you to their mailing list informing you of company updates and new products.
It won’t harm you or your organization, but it can be annoying to receive emails you never wanted.
You can generally unsubscribe from these lists, or you can block the sender so the messages will be redirected to your junk folder rather than your inbox.
What is Phishing?
Phishing messages are bulk emails that appear to be from a legitimate source asking you to take a specific action that can cause harm to you or your organization.
These messages should be reported to an IT administrator so they can take the proper steps to make sure similar emails don’t reach other employees at your company.
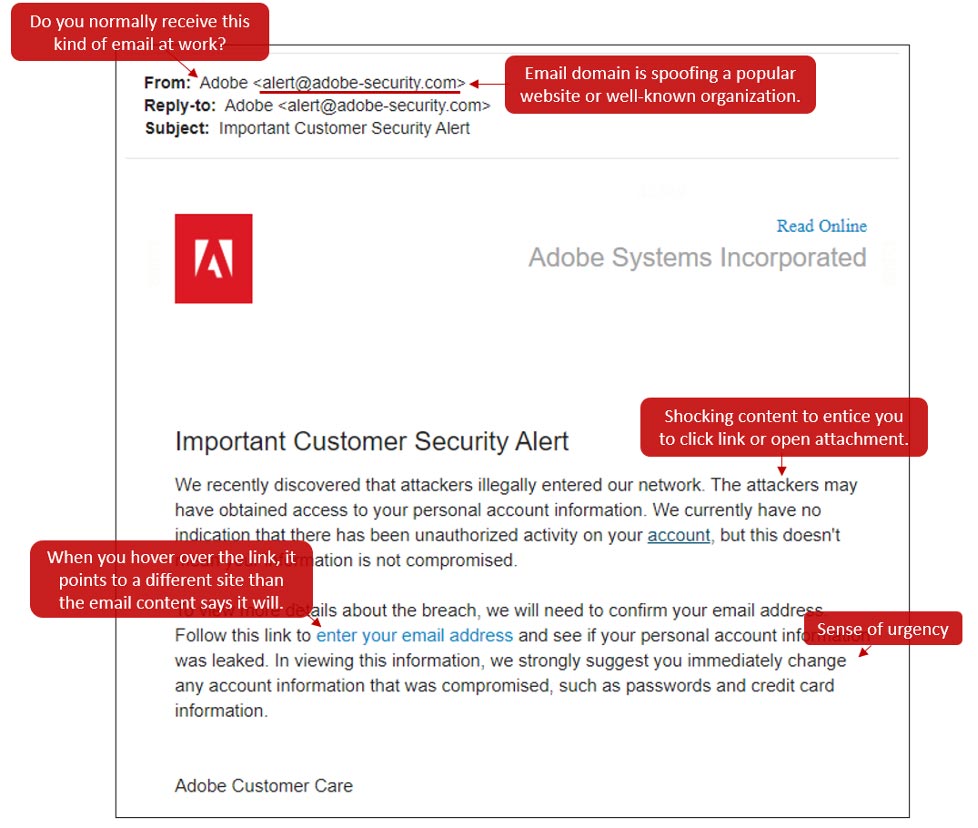
Here’s an example of a phishing attempt from someone or something claiming to be Adobe to steal username and password information.
There are a lot of clues that make it easy to figure out this is not a legitimate email from Adobe.
- Do you normally receive this kind of email at work?
- Email domain is spoofing a popular website or well-known organization.
- Shocking content to entice you to click link or open attachment.
- When you hover over the link, it points to a different site than the email content says it will.
- Sense of urgency
Most phishing attempts want you to act ASAP to force you to make irrational decisions and not think about the validity of the email.
Other examples could be someone posing as the CEO of your company asking an employee to make a purchase on their behalf, potentially asking the employee to send credit card or other sensitive information.
A good rule of thumb is to never send personal information via email.
Here is a checklist of things to look for when determining if an email is a phishing attempt:
- Make sure the “from” email address is legitimate (look for misspellings or addresses that don’t match who or what they are claiming to be)
- Misspelled words
- Requests for personal or sensitive information
- URLs that direct to unofficial sites
- The action requested needs to happen immediately or ASAP
If you’re still unsure whether an email is potentially harmful, contact your IT administrator.
Spam is Harmless, Phishing is Malicious
The big takeaway is spam is usually harmless and won’t ask for personal information to steal your identity. Phishing messages, on the other hand, are designed to steal personal information and cause harm to you and others in your organization.
Looking to protect your company from cybersecurity threats? Contact Hungerford Technologies at (616) 949-4020 to learn how we can help secure your sensitive data.